Social Media & Politics: A Changing Landscape

“`html
The Expanding Influence of Social Media on Political Landscapes
Social media has fundamentally reshaped the way politics operates, evolving from a supplementary tool to an indispensable force. It’s no longer just about politicians having official Facebook pages; it’s about how campaigns are built, messages are disseminated, and public opinion is swayed – all within the complex ecosystem of platforms like Twitter (now X), Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and many others. This post will delve into the multifaceted role social media plays in modern politics, exploring both its benefits and drawbacks.
The Rise of Social Media in Political Campaigns
Historically, political campaigns relied heavily on traditional media: television advertising, newspaper endorsements, radio spots, and rallies. While these remain relevant to some extent, they’ve been dramatically augmented – and in many cases, overshadowed – by social media strategies.
Direct Voter Engagement: Social media allows candidates to communicate directly with voters without the filter of traditional media. They can answer questions, address concerns in real-time, and build a sense of personal connection. This immediacy is powerful. Live Q&A sessions on platforms like Instagram or Twitter provide opportunities for authentic engagement that wasn’t possible before.
Microtargeting: Social media platforms collect vast amounts of data about their users—their interests, demographics, online behavior. Campaigns leverage this data to create highly targeted advertising campaigns. Instead of a blanket message aimed at all voters, they can craft specific ads tailored to different segments of the population, maximizing impact and efficiency.
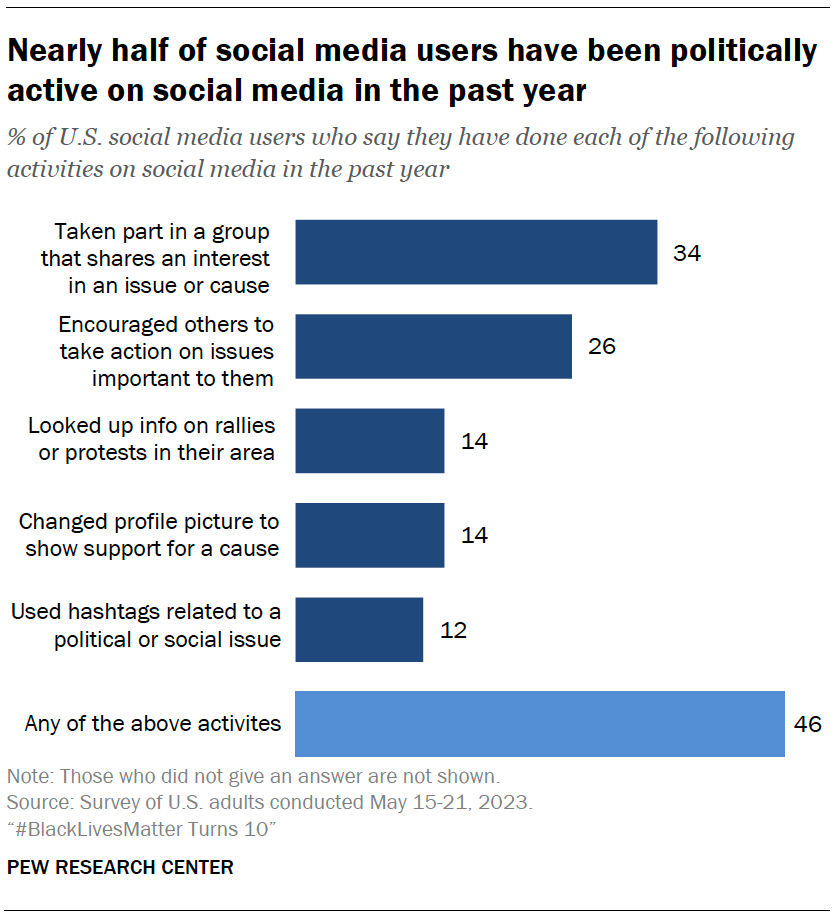
Grassroots Mobilization: Social media has proven incredibly effective for mobilizing supporters and volunteers. Events can be organized quickly through Facebook groups or event pages. Sharing information about rallies and protests becomes instantaneous, fostering a sense of community and encouraging participation. The ability to share content virally allows grassroots movements to gain significant traction.
Fundraising: Online fundraising has become an essential component of modern political campaigns, and social media is a key driver. Small-dollar donations can be solicited through targeted ads or organic posts, often accompanied by compelling narratives or urgent appeals.
The Downsides & Challenges
While the benefits are clear, social media’s influence on politics isn’t without significant drawbacks and challenges. The potential for misuse is substantial.
Misinformation and Disinformation
The Spread of False Information: Social media platforms are often breeding grounds for misinformation (unintentional inaccuracies) and disinformation (deliberate falsehoods). Fake news stories, conspiracy theories, and manipulated videos can spread rapidly through social networks, reaching millions before they can be debunked. The algorithms that prioritize engagement – even if it’s negative or false—can inadvertently amplify these harmful narratives.
Echo Chambers & Polarization: Social media algorithms often create “echo chambers” where users are primarily exposed to information and perspectives that confirm their existing beliefs. This reinforces biases, leading to increased polarization and making constructive dialogue more difficult. People become less likely to encounter opposing viewpoints, solidifying extreme positions.
Bots & Foreign Interference: Malicious actors—including foreign governments—can use bots (automated accounts) to spread disinformation, sow discord, and influence elections. These bots can amplify divisive messages, impersonate real users, and create a false impression of widespread support for certain candidates or policies.
Privacy Concerns
Data Harvesting & Manipulation: The extensive data collection practices of social media platforms raise serious privacy concerns. Campaigns’ ability to target voters based on sensitive personal information can be exploited in ways that undermine democratic principles. Concerns about the use of this data for manipulative purposes are legitimate.
The Impact on Political Discourse
Shortened Attention Spans & Sound Bites: Social media favors short, catchy content over nuanced discussion. This can lead to a simplification of complex political issues and an emphasis on emotional appeals rather than reasoned arguments. The focus shifts from substance to style.
Increased Toxicity & Harassment: The anonymity afforded by social media can embolden individuals to engage in abusive or harassing behavior, targeting politicians, journalists, and ordinary citizens alike. This toxic environment can discourage participation and stifle free speech.
Navigating the New Political Landscape
So, what can be done to mitigate the negative impacts of social media on politics while harnessing its potential for good?
Media Literacy & Critical Thinking
Educating Voters: Improving media literacy among voters is crucial. Individuals need to develop the skills to critically evaluate information they encounter online, identify bias, and distinguish between credible sources and misinformation.
Platform Accountability
Regulation & Oversight: Social media platforms face increasing pressure to take responsibility for the content that appears on their sites. This includes implementing stricter policies against disinformation, combating bot networks, and improving transparency around political advertising. Government regulation may be necessary to hold these companies accountable.
Promoting Constructive Dialogue
Encouraging Civil Discourse: Efforts to foster constructive dialogue across ideological divides are essential. This can involve promoting respectful online conversations, encouraging cross-partisan collaborations, and creating spaces for productive debate.
The Future of Social Media & Politics
Social media’s role in politics will only continue to evolve. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and the metaverse are likely to further transform the political landscape, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Understanding these trends is crucial for safeguarding democratic processes and ensuring a healthy public sphere.
The Rise of TikTok: The growing popularity of platforms like TikTok, with its short-form video format, presents new avenues for political messaging – and potential risks related to misinformation and fleeting attention spans.
Ultimately, the responsibility for navigating this complex landscape rests not only on social media companies and governments but also on individual citizens. By being informed, critical consumers of information and engaging in respectful dialogue, we can help shape a future where social media contributes positively to democratic participation.
“`