Level Up: The Explosive Growth of Esports

The Meteoric Rise of Esports: From Niche Hobby to Global Phenomenon
For many, the image of gaming conjures up thoughts of solitary players lost in virtual worlds. However, a dramatic shift has occurred over the last two decades. Gaming has exploded into a spectator sport, a multi-billion dollar industry, and a legitimate career path for thousands. This is the world of esports – competitive video gaming – and its growth has been nothing short of phenomenal.
A Brief History: From Arcades to Arenas
The roots of esports can be traced back to the early days of video games. In 1972, Stanford University hosted what is widely considered the first video game competition, a Spacewar! tournament. Throughout the 1980s, arcade games like Pac-Man and Donkey Kong fueled local high-score competitions. These were largely informal, but they laid the groundwork for organized play.
The 1990s saw the emergence of PC gaming and the internet, which proved to be a pivotal moment. Games like Doom and Quake were popular choices for early online multiplayer matches, and leagues began to form. The first professional gaming league, the Cyberathlete Professional League (CPL), was founded in 1997, marking a significant step towards the modern esports landscape. Early internet connectivity limitations meant these events were still relatively small, but the seeds were sown.
The early 2000s brought increased bandwidth and more sophisticated gaming titles. StarCraft: Brood War became a massive hit in South Korea, where it evolved into a national obsession with professional players achieving celebrity status. This period demonstrated the potential for esports to become a mainstream form of entertainment. Games like Counter-Strike and Warcraft III also gained traction, building dedicated communities and competitive scenes.
The Modern Esports Landscape: Games, Teams, and Leagues
Today, esports encompasses a vast array of games, each with its own dedicated following. Some of the most popular titles include:
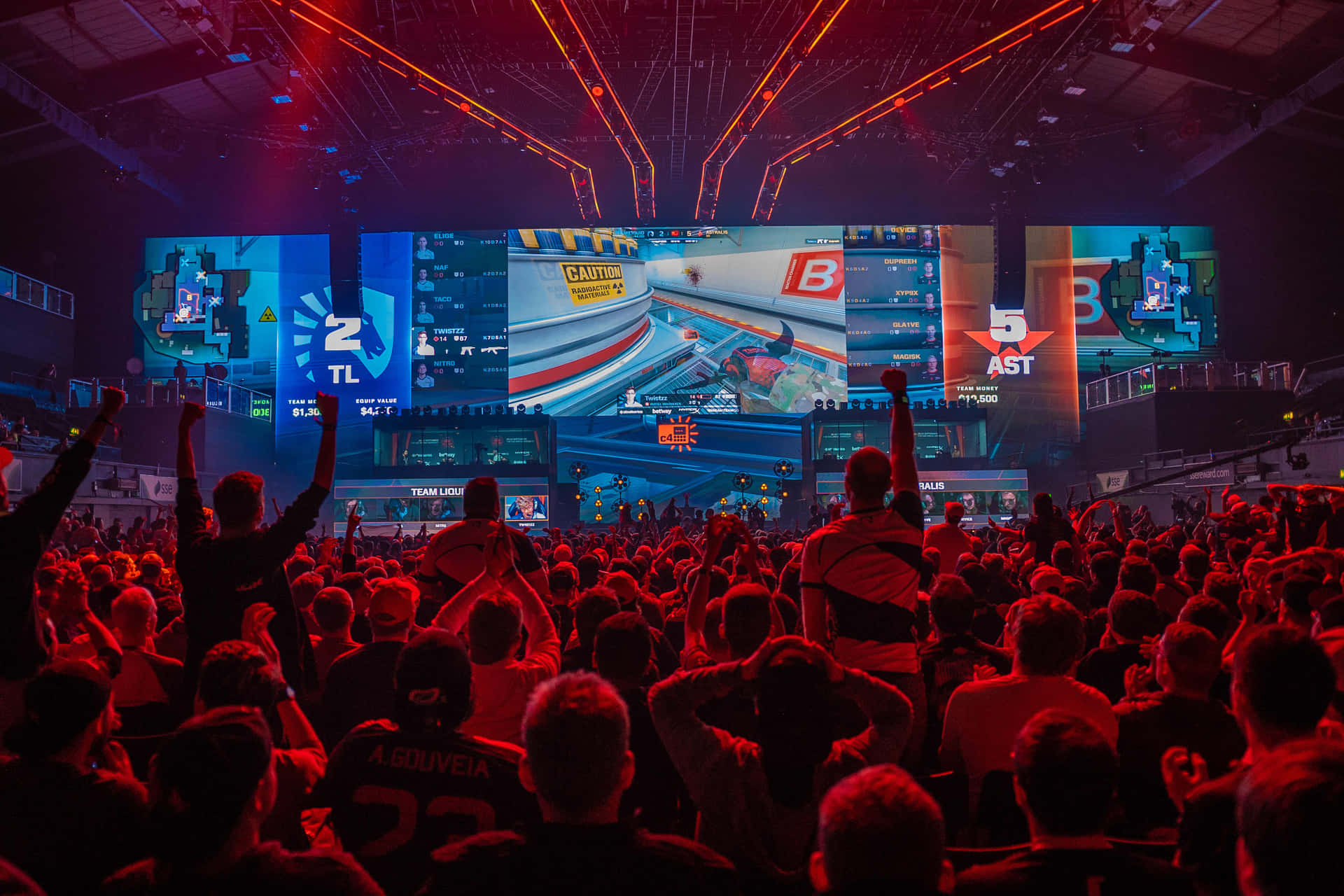

- League of Legends (LoL): A multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA) game developed by Riot Games. LoL consistently boasts the highest viewership numbers in esports.
- Dota 2: Another highly popular MOBA, known for its complex gameplay and massive prize pools.
- Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (CS:GO): A tactical first-person shooter (FPS) that remains a staple of the esports scene.
- Valorant: A newer FPS title from Riot Games, quickly gaining popularity with its strategic gameplay.
- Overwatch 2: A team-based hero shooter known for its diverse cast of characters and fast-paced action.
- Fortnite: A battle royale game that has captivated a massive audience, particularly among younger players.
- Call of Duty: A long-running FPS franchise with a thriving competitive scene.
Professional esports teams, often sponsored by major brands, compete in organized leagues and tournaments. These teams employ players, coaches, analysts, and support staff. Some of the most well-known organizations include Team Liquid, FaZe Clan, G2 Esports, and TSM. The level of professionalism is continually increasing, with teams investing heavily in training facilities, player development, and strategic analysis.
Major esports leagues, such as the League of Legends Championship Series (LCS), the Dota Pro Circuit (DPC), and the Overwatch League (OWL), provide structured competition throughout the year. These leagues feature regular season play, playoffs, and championship events. Independent tournament organizers, like ESL and DreamHack, also host prestigious events with substantial prize pools.
The Business of Esports: Revenue Streams and Growth
The esports industry is a booming business. Revenue is generated through a variety of sources:
Sponsorships: Brands are eager to associate themselves with the growing esports audience, leading to lucrative sponsorship deals with teams, leagues, and events. Non-endemic sponsors (companies not traditionally associated with gaming) are becoming increasingly common.
Media Rights: Broadcasting rights for esports events are becoming increasingly valuable. Platforms like Twitch, YouTube, and even traditional television networks are vying for the rights to air competitions.
Advertising: Advertising within esports broadcasts and online content generates significant revenue.
Merchandise: Teams and leagues sell merchandise, such as jerseys, apparel, and accessories.
Ticket Sales: Large-scale esports events attract thousands of spectators, generating revenue through ticket sales.
In-Game Purchases: Some games incorporate cosmetic items or other in-game purchases that contribute to the esports ecosystem.
The global esports market is projected to continue its rapid growth, with estimates suggesting it will surpass $1.6 billion in revenue in 2023. This growth is fueled by increasing viewership, expanding demographics, and growing investment from traditional sports organizations.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its success, esports faces several challenges. Maintaining player health and well-being is a concern, as professional gamers often endure long hours of practice and competition. Issues related to match-fixing and cheating also need to be addressed. Furthermore, the industry needs to continue to diversify its audience and promote inclusivity.
Looking ahead, the future of esports appears bright. The increasing integration of esports into mainstream culture, the potential for inclusion in the Olympic Games, and the continued development of new gaming technologies will likely drive further growth. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) could revolutionize the esports experience, creating immersive and interactive viewing environments. The rise of mobile esports is also a significant trend, opening up new opportunities for players and fans. Esports is no longer a fleeting trend; it’s a legitimate and rapidly evolving form of entertainment that is here to stay.