Data-Driven Decisions: A Guide for Small Businesses
Data Analytics: Your Secret Weapon for Small Business Success
For years, “data analytics” felt like a buzzword reserved for massive corporations with sprawling data science teams. But the truth is, harnessing the power of data doesn’t require a PhD or a six-figure budget. In today’s competitive landscape, even small businesses can – and *need* to – leverage data analytics to make smarter decisions, understand their customers better, and ultimately, drive growth.
This post aims to demystify data analytics for small business owners, explaining what it is, why it’s crucial, and most importantly, how you can start using readily available tools *today* to gain a significant advantage. We’ll break down the core concepts and provide practical examples so you can see the real-world impact of data-driven decision making.
What Exactly Is Data Analytics?
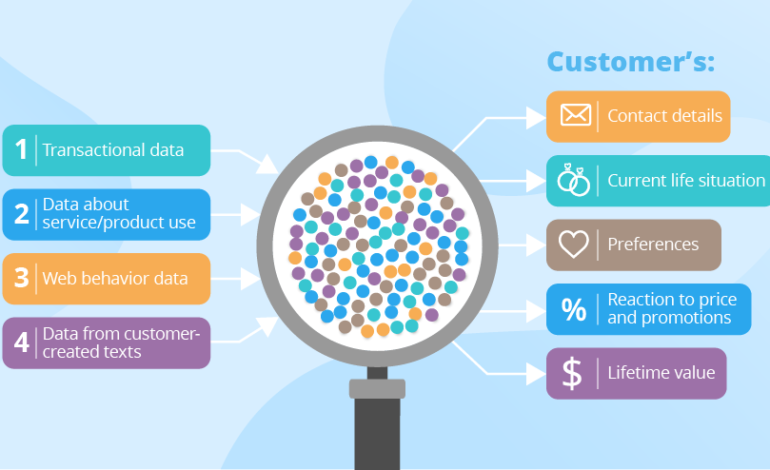
At its core, data analytics is the process of examining raw data to draw conclusions about that information. It’s not just about collecting numbers; it’s about interpreting them and turning those interpretations into actionable insights. Think of it as detective work for your business – you’re searching for clues hidden within your data to reveal patterns, trends, and opportunities.
Different Types of Data Analytics
- Descriptive Analytics: This is the most basic type. It answers the question “What happened?”. It involves summarizing historical data – things like sales figures over time, website traffic statistics, or customer demographics.
- Diagnostic Analytics: Moves beyond “what” to explore *why*. For example, why did sales decline last month? Diagnostic analytics uses techniques like correlation analysis to identify potential causes.
- Predictive Analytics: Looks forward and tries to predict future outcomes based on past data. “What is likely to happen?”. This might involve forecasting sales for the next quarter or predicting which customers are most likely to churn.
- Prescriptive Analytics: The most advanced type, suggesting actions to take. “What should we do?”. For example, if predictive analytics forecasts a dip in sales, prescriptive analytics might recommend launching a targeted marketing campaign.
Why Should Small Businesses Care About Data Analytics?
You might be thinking, “I’m a small business owner, not a data scientist! Why should I bother?” The answer is simple: data-driven decisions are better decisions. Here’s how data analytics can benefit your small business:

- Understand Your Customers Better: What products do they buy most often? What channels do they use to find you (website, social media, email)? Where are they located? Data helps you build detailed customer profiles.
- Improve Marketing Effectiveness: Are your marketing campaigns actually working? Analytics can track campaign performance, identify which ads are driving the best results, and help you optimize your spending.
- Identify Growth Opportunities: Spot emerging trends in customer behavior or market demand. Perhaps there’s a new product line you should consider, or a geographic area you haven’t explored yet.
- Reduce Costs & Increase Efficiency: Identify areas where you’re wasting resources (e.g., inefficient marketing spend, high shipping costs) and take steps to improve operations.
- Gain a Competitive Advantage: By understanding your customers and market better than your competitors, you can position yourself for success.
Easy-to-Use Data Analytics Tools for Small Businesses
The good news is that you don’t need expensive software or a team of experts to get started. Here are some readily available tools most small businesses can use:
1. Google Analytics
Free and incredibly powerful, Google Analytics tracks website traffic, user behavior, and conversions. You can see where your visitors come from (referral sources), what pages they visit, how long they stay on your site, and much more. This data is crucial for understanding the effectiveness of your online marketing efforts.
- Key Metrics to Track: Bounce Rate, Session Duration, Pageviews, Conversion Rate
2. Google Search Console
Another free tool from Google, Search Console helps you monitor your website’s performance in search results. It provides insights into keyword rankings, click-through rates, and technical issues that might be hindering your SEO.
3. Social Media Analytics (Facebook Insights, Twitter Analytics, Instagram Insights)
Most social media platforms offer built-in analytics dashboards. These provide valuable data on follower demographics, engagement rates (likes, comments, shares), and the performance of individual posts. Use this information to tailor your content strategy and maximize reach.
4. Email Marketing Platforms (Mailchimp, Constant Contact)
If you use email marketing, leverage the analytics provided by your platform. Track open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates to see which emails are most effective and optimize your campaigns accordingly. Many platforms also offer A/B testing features so you can experiment with different subject lines or content.
5. Point of Sale (POS) Systems
If you have a brick-and-mortar store, your POS system likely collects valuable sales data. Analyze this data to identify best-selling products, peak shopping times, and customer purchase patterns. Some POS systems even offer built-in reporting features.
6. Spreadsheets (Google Sheets, Microsoft Excel)
Don’t underestimate the power of a simple spreadsheet! You can manually enter and analyze data from various sources to identify trends and gain insights. This is particularly useful for small businesses that don’t have sophisticated analytics tools in place.
Getting Started: Small Steps, Big Impact
You don’t need to implement everything at once. Start with one or two areas where you think data can make a significant difference. For example:
- Track Website Traffic: Set up Google Analytics and monitor your most popular pages and referral sources.
- Analyze Social Media Performance: Look at your engagement metrics on Facebook, Twitter, or Instagram to see what content resonates with your audience.
- Review Sales Data: Analyze your POS data to identify your best-selling products and customer purchase patterns.
As you become more comfortable with data analytics, you can explore more advanced techniques and tools. The key is to start small, be consistent, and use the insights you gain to make informed decisions.
Conclusion: Embrace Data for a Brighter Future
Data analytics isn’t just for big businesses anymore. It’s an essential tool for any business that wants to thrive in today’s competitive market. By embracing data-driven decision making, small businesses can level the playing field and achieve remarkable results. So, take the first step today – start exploring your data and unlock its hidden potential!



