Cybersecurity Essentials for Businesses
Cybersecurity: A Business Imperative in 2024
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, cybersecurity isn’t just an IT concern; it’s a fundamental business imperative. Businesses of all sizes – from startups to multinational corporations – are facing increasingly sophisticated and frequent cyberattacks. Failing to prioritize robust security measures can lead to devastating consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, legal liabilities, and operational disruption. This post will delve into the emerging cyber threats businesses face in 2024 and outline essential security measures they need to implement to protect their assets.
The Current Threat Landscape: A Growing Tide of Attacks
Let’s be clear: the threat landscape isn’t static; it’s constantly shifting. What worked last year might not cut it today. Here’s a breakdown of some key emerging threats:
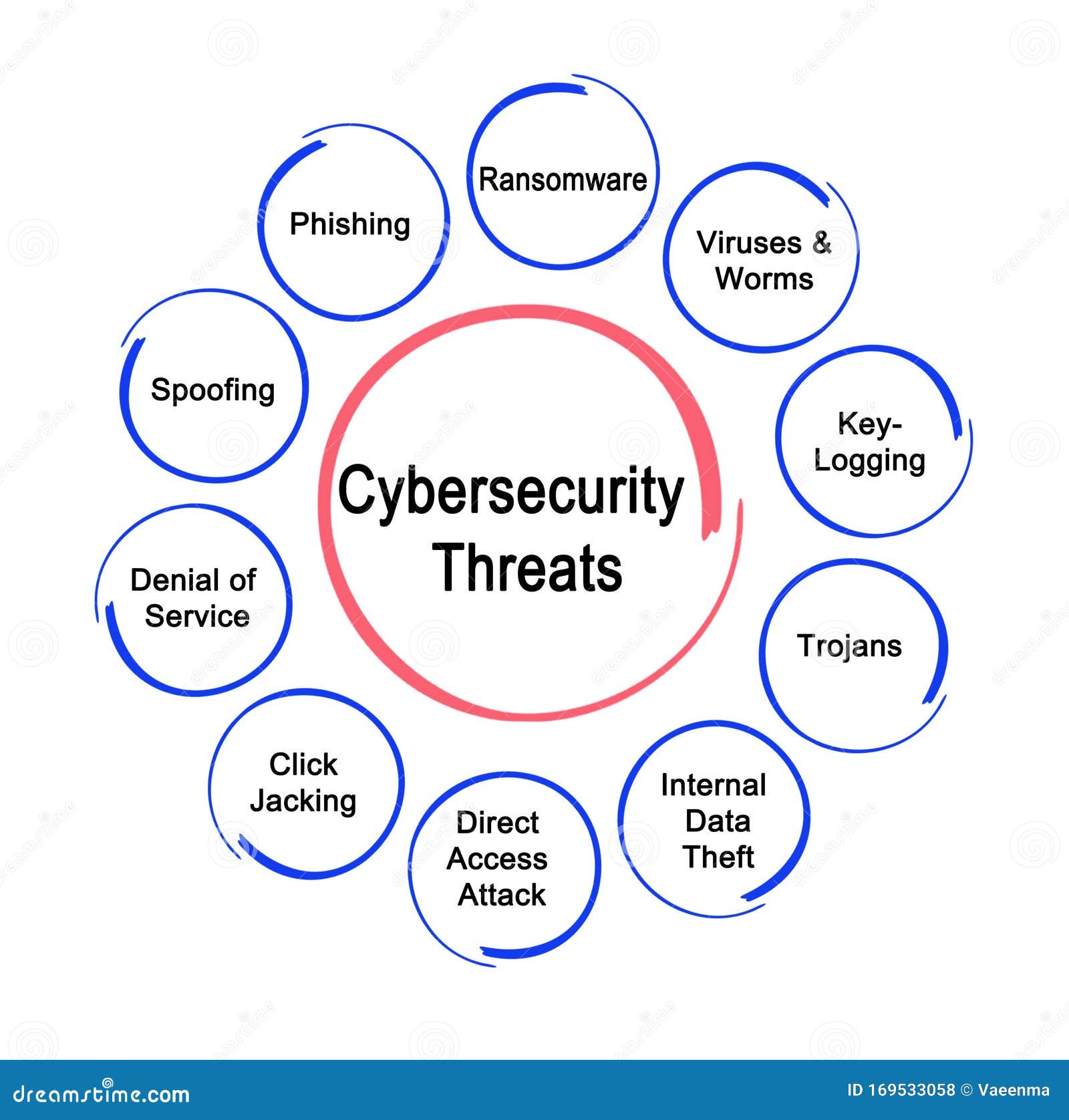
- Ransomware: Still a dominant force, ransomware attacks are becoming more targeted and sophisticated. Attackers aren’t just encrypting data; they’re often exfiltrating it first, threatening to release sensitive information if the ransom isn’t paid (double extortion). Triple extortion is also on the rise, involving DDoS attacks alongside data encryption and theft.
- Phishing & Spear Phishing: These remain incredibly effective due to human error being a common vulnerability. Spear phishing targets specific individuals within an organization with highly personalized emails designed to appear legitimate. AI is now being leveraged to craft even more convincing phishing campaigns, making them harder to detect.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Attackers are increasingly targeting third-party vendors and suppliers to gain access to their clients’ systems. A vulnerability in a single vendor can compromise numerous downstream businesses. The SolarWinds attack serves as a stark reminder of the potential impact of these attacks.
- Cloud Vulnerabilities: As more businesses migrate to cloud services, misconfigured cloud environments are becoming a prime target for attackers. Lack of visibility and control over cloud resources can leave organizations exposed.
- IoT (Internet of Things) Exploitation: The proliferation of IoT devices – from smart thermostats to industrial sensors – creates new entry points for hackers. Many IoT devices have weak security protocols, making them easy targets.
- AI-Powered Attacks: Cybercriminals are starting to leverage AI to automate tasks like vulnerability scanning, phishing campaign creation, and malware development, increasing the scale and efficiency of their attacks.
- Insider Threats: These can be malicious (intentional) or negligent (unintentional). Disgruntled employees or those who simply make mistakes can inadvertently expose sensitive data.
Essential Cybersecurity Measures for Businesses
Now that we’ve examined the threats, let’s move on to the proactive measures businesses need to take. A layered approach is crucial – relying on a single security tool isn’t enough.
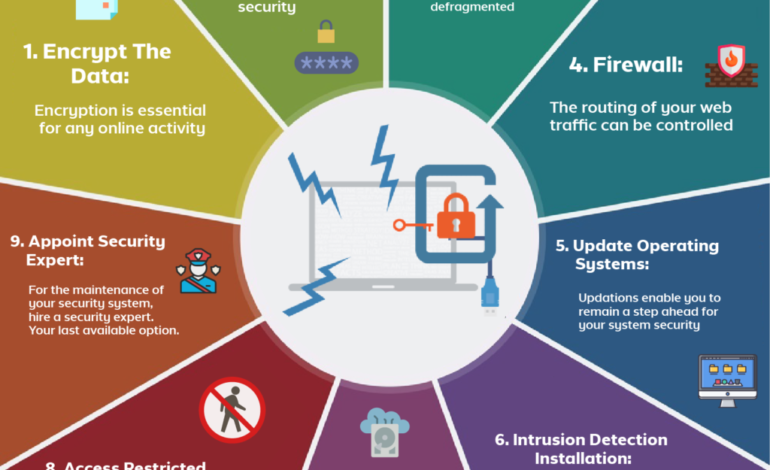
1. Foundational Security Practices
- Strong Passwords & Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): This should be non-negotiable. Enforce strong password policies and mandate MFA for all accounts, especially those with privileged access.
- Regular Software Updates & Patching: Outdated software is a major vulnerability. Implement a system to regularly patch operating systems, applications, and firmware on all devices. Automate this process where possible.
- Firewalls & Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These form the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Ensure your firewalls are properly configured and regularly updated with threat intelligence feeds.
- Endpoint Security: Implement endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to monitor endpoints for malicious activity, detect threats, and respond quickly. Traditional antivirus software is often insufficient.
2. Advanced Strategies
- Network Segmentation: Divide your network into smaller segments to limit the impact of a potential breach. If one segment is compromised, attackers won’t have free rein over the entire network.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP solutions to monitor and control sensitive data leaving your organization’s perimeter, preventing accidental or malicious exfiltration.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): A SIEM system collects security logs from various sources and correlates them to identify potential threats in real-time.
- Vulnerability Scanning & Penetration Testing: Regularly scan your systems for vulnerabilities and conduct penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks and identify weaknesses.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Specifically important for businesses utilizing cloud services, CSPM tools continuously monitor cloud environments for misconfigurations and security risks.
3. Human Factor & Training
- Cybersecurity Awareness Training: Educate employees about common cyber threats like phishing and social engineering. Conduct regular training sessions to reinforce best practices. Simulate phishing attacks to test employee awareness.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a detailed incident response plan that outlines procedures for handling security incidents, including containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis. Test the plan regularly through tabletop exercises.
- Background Checks & Access Control: Conduct thorough background checks on employees with access to sensitive data. Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to limit access only to what is necessary for job functions.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Cybersecurity
The cybersecurity landscape will continue to evolve, demanding constant adaptation from businesses. Here are some trends to watch:
- Increased AI Adoption in Security: Both attackers and defenders will increasingly leverage AI. Organizations need to invest in AI-powered security solutions to stay ahead of the curve.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Moving away from traditional perimeter-based security towards a “never trust, always verify” model is becoming essential.
- Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture (CSMA): This approach allows for more flexible and adaptable security controls across distributed environments, especially vital with the rise of hybrid cloud deployments.
- Quantum Computing Threat: While still emerging, the potential of quantum computing to break current encryption algorithms is a long-term concern that organizations need to plan for.
Conclusion: Proactive Protection is Paramount
Cybersecurity isn’t just an expense; it’s an investment in your business’s survival and success. Ignoring the growing threat landscape or failing to implement appropriate security measures can have catastrophic consequences. By adopting a layered approach that encompasses technology, processes, and people, businesses can significantly reduce their risk of cyberattacks and protect their valuable assets.



