Blockchain Beyond Bitcoin: Exploring Diverse Applications

Beyond Bitcoin: Exploring the Diverse Applications of Blockchain Technology
When most people hear the word “blockchain,” their minds immediately jump to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. While blockchain technology *is* foundational to these digital currencies, its potential extends far beyond simply enabling transactions involving virtual money. In fact, blockchain’s unique characteristics – decentralization, immutability, and transparency – make it a powerful tool applicable across a surprisingly wide range of industries. This post will delve into the world of blockchain, moving past the cryptocurrency hype to explore its burgeoning applications in areas like supply chain management, healthcare, digital identity, and more.
Understanding Blockchain Basics: More Than Just a Cryptocurrency Ledger
Before we dive into specific applications, let’s quickly recap what blockchain actually *is*. At its core, a blockchain is a distributed, immutable ledger. Let’s break that down:
- Distributed: Instead of being stored in one central location (like a traditional database), the blockchain exists across many computers simultaneously. This removes the single point of failure and makes it incredibly resistant to hacking or manipulation.
- Immutable: Once data is added to the blockchain, it’s extremely difficult – practically impossible – to change or delete it. Each new block of data contains a cryptographic “hash” of the previous block, creating an unbreakable chain. Any attempt to alter a past record would invalidate all subsequent blocks.
- Ledger: Essentially, a record book. It tracks transactions or any other type of information agreed upon by the network participants.
Think of it as a shared, secure spreadsheet that everyone on the network can see, but no one can unilaterally alter without consensus.
Blockchain in Supply Chain Management: Tracking Goods from Origin to Consumer
Supply chain management is notoriously complex, often involving numerous intermediaries, disparate systems, and a lack of transparency. Blockchain offers a compelling solution by providing an end-to-end view of the entire supply chain process. Here’s how:
- Provenance Tracking: Imagine tracking a coffee bean from the farm in Colombia to your cup. With blockchain, every step – harvesting, processing, shipping, roasting, packaging – can be recorded on an immutable ledger. Consumers can scan a QR code and instantly verify the origin of their product, ensuring authenticity and ethical sourcing.
- Reduced Counterfeiting: Blockchain’s immutability makes it incredibly difficult to introduce counterfeit goods into the supply chain. Each item can be assigned a unique identifier on the blockchain, allowing for verification at any point in its journey.
- Improved Efficiency & Reduced Costs: By automating processes like invoicing and payment using smart contracts (self-executing agreements written into code), blockchain can streamline operations and reduce administrative overhead.
- Enhanced Transparency & Accountability: All stakeholders – suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers – have access to the same information, fostering trust and accountability throughout the chain. Walmart, for example, is already using blockchain to track pork in China and mangoes in the United States, significantly improving traceability and food safety.
Revolutionizing Healthcare with Blockchain: Security & Interoperability
The healthcare industry faces numerous challenges including data security breaches, lack of interoperability between systems, and difficulties in patient identity management. Blockchain can address these issues:
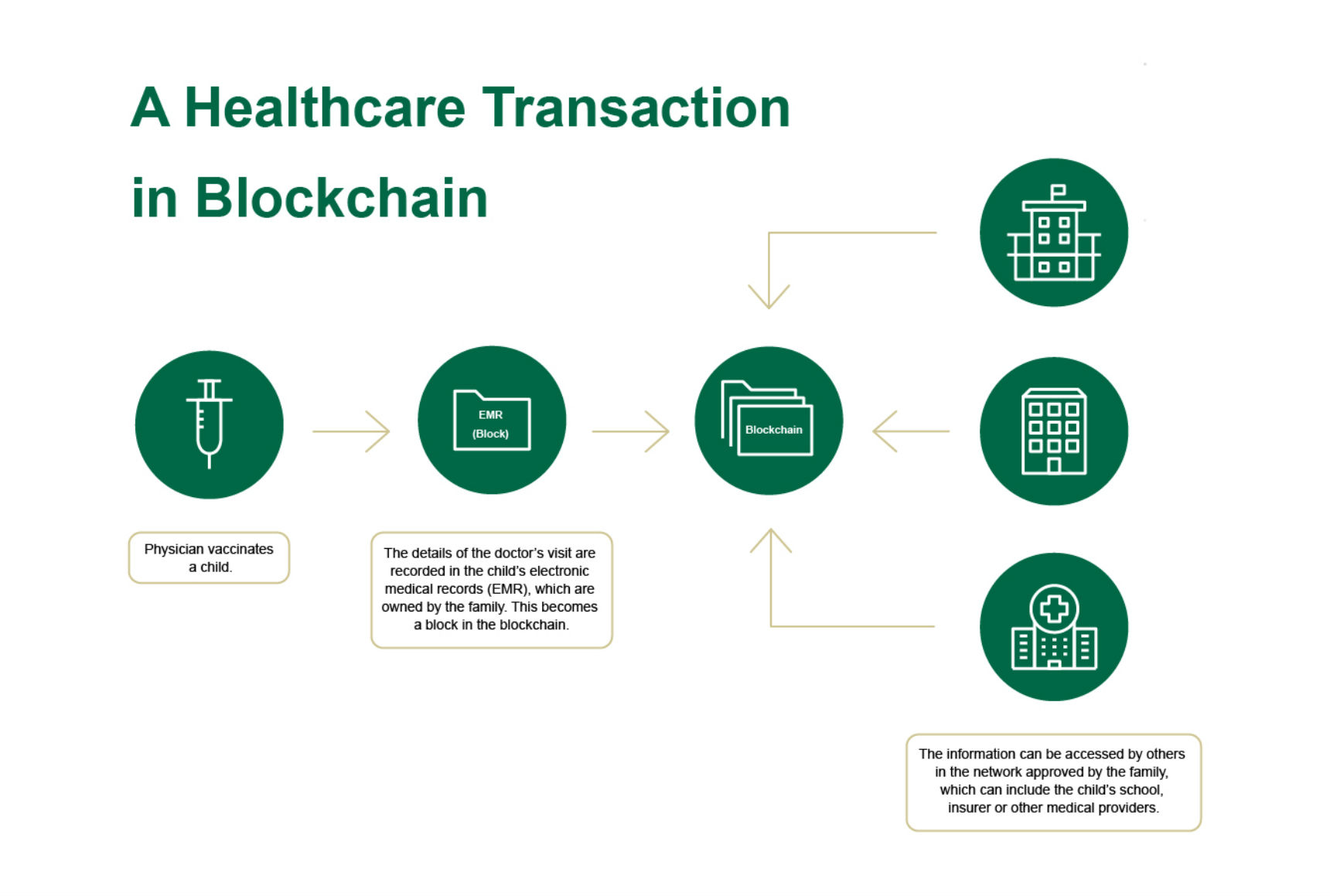
- Secure Patient Records Management: Patients could have control over their own medical records stored on a blockchain. This allows them to grant access to specific healthcare providers as needed, improving data privacy and portability.
- Drug Supply Chain Security: Combating counterfeit drugs is a major concern. Blockchain can track pharmaceuticals from manufacturer to patient, ensuring authenticity and preventing the introduction of fake medications into the system.
- Clinical Trial Management: Blockchain can improve the integrity and transparency of clinical trials by securely recording data and tracking participant consent.
- Interoperability: Different healthcare systems often struggle to communicate effectively due to incompatible formats. Blockchain can provide a common platform for sharing patient data securely and efficiently, promoting better care coordination.
Digital Identity Management: Taking Control of Your Personal Data
In today’s digital age, managing our online identities is increasingly complex. Blockchain offers a promising solution for self-sovereign identity (SSI), where individuals have complete control over their personal data.
- Decentralized Identity Verification: Instead of relying on centralized authorities like Facebook or Google to verify your identity, you can store and manage your credentials on a blockchain.
- Selective Disclosure: You can choose exactly which pieces of information you share with different entities – for example, proving you’re over 21 without revealing your date of birth.
- Reduced Fraud & Identity Theft: Blockchain’s security features make it more resistant to identity theft and fraud.
- Streamlined KYC/AML Compliance: For businesses, blockchain-based identity solutions can simplify Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance processes.
Beyond the Big Three: Other Promising Applications
The applications discussed above are just the tip of the iceberg. Blockchain is being explored in numerous other sectors:
- Voting Systems: Enhancing security and transparency in elections through immutable, auditable records.
- Intellectual Property Rights Management: Protecting copyrights and trademarks by registering them on a blockchain.
- Real Estate: Streamlining property transactions and reducing fraud by recording ownership and transfer deeds on a blockchain.
- Gaming: Creating truly owned in-game assets (NFTs – Non-Fungible Tokens) that players can buy, sell, and trade.
Challenges & Future Outlook
While the potential of blockchain is undeniable, challenges remain:
- Scalability: Some blockchains struggle to handle a large volume of transactions efficiently. Solutions like layer-2 scaling are being developed to address this issue.
- Regulation: The regulatory landscape for blockchain technology is still evolving, creating uncertainty for businesses.
- Complexity: Developing and deploying blockchain solutions can be technically challenging.
Despite these challenges, the future of blockchain looks bright. As the technology matures and adoption increases, we are likely to see even more innovative applications emerge across diverse industries. The shift from viewing blockchain solely as a cryptocurrency enabler to recognizing its broader potential is well underway – positioning it as a transformative technology for years to come.



