Excel Power User Tips & Tricks
Mastering Excel: Tips and Tricks for Power Users
Excel. The name alone can evoke a mix of excitement and dread in many people. While it’s often touted as an essential tool for professionals across various industries, its vast capabilities are frequently underutilized. Most users stick to basic functions like SUM and AVERAGE, unaware of the wealth of advanced features that Excel holds. This post aims to unlock those hidden powers, providing tips and tricks designed to elevate your Excel skills from novice to power user.
Understanding Formulas: Beyond the Basics
Let’s start with formulas – the backbone of Excel’s functionality. You probably know how to add numbers using SUM(), but there’s a whole universe beyond that.
Relative vs. Absolute References: This is crucial for accurate calculations when copying formulas. Relative references (like A1) change based on where you copy the formula. Absolute references (like $A$1) remain fixed. To make a reference absolute, use the dollar sign ($). For example, if you want to subtract a constant value from many cells, using an absolute reference like =$10 ensures that every cell’s calculation uses 10.
Logical Functions (IF, AND, OR): These functions allow for conditional calculations. The IF() function executes different actions based on whether a condition is true or false. You can nest IF() statements to create complex decision-making processes within your spreadsheets. Combine these with AND and OR for even more sophisticated logic.
Lookup Functions (VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, INDEX/MATCH): These are incredibly powerful when dealing with large datasets. VLOOKUP searches a table column by row and returns a value from another column in the same row. HLOOKUP works similarly but searches horizontally. However, INDEX/MATCH is generally preferred as it’s more flexible and less prone to errors (especially when adding or deleting columns). INDEX returns a value at a specific intersection of rows and columns; MATCH finds the position of an item in a range.
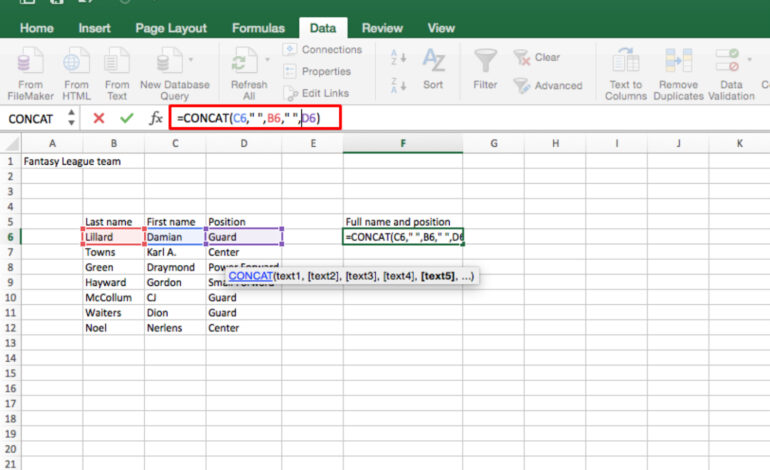
Text Functions (LEFT, RIGHT, MID, CONCATENATE): Manipulating text data is common. LEFT() extracts characters from the left side of a string, RIGHT() from the right, and MID() from the center. CONCATENATE combines multiple strings into one.
Data Analysis Tools: Unveiling Insights
Excel isn’t just for calculations; it’s also a powerful data analysis tool.
PivotTables: These are game-changers for summarizing and analyzing large datasets. You can quickly create interactive reports, group data, filter results, and calculate aggregates (SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT) with ease. Experiment with different layouts and fields to explore your data from various angles.
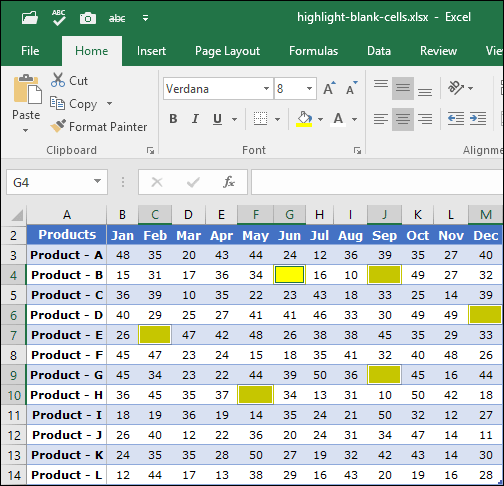
Conditional Formatting: Highlight important trends and anomalies in your data visually. You can apply rules based on cell values, formulas, or even icons. For example, you could highlight all sales figures above a certain threshold in green and those below in red.
Data Validation: Ensure data integrity by restricting the type of data that users can enter into cells. This prevents errors and inconsistencies. You can create dropdown lists, number ranges, or custom criteria.
Efficiency Boosters: Saving Time & Effort
Let’s move on to techniques that will streamline your workflow and save you precious time.
Keyboard Shortcuts: Learn the essential shortcuts! Ctrl+C (Copy), Ctrl+V (Paste), Ctrl+Z (Undo), Ctrl+X (Cut), Ctrl+A (Select All), Ctrl+S (Save) are just the beginning. Research and memorize others specific to your tasks.
Quick Access Toolbar: Customize this toolbar with frequently used commands for instant access.
Ribbon Customization: Add commonly used features directly to the ribbon, reducing clicks and increasing efficiency.
Recording Macros: Automate repetitive tasks by recording macros. Excel will record your actions and allow you to replay them with a single click. This is incredibly useful for complex data entry or formatting processes. You can even write VBA code (Visual Basic for Applications) to further customize your macros.
Flash Fill: Excel’s Flash Fill feature intelligently recognizes patterns in your data and automatically fills in the rest of the column. For example, if you have a list of full names and want to split them into first and last name columns, Excel can often do it for you with just a few examples.
Advanced Features: Taking Excel to the Next Level
Now let’s delve into some more advanced features that separate true Excel power users from the rest.
Power Query (Get & Transform Data): This is an ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tool built directly into Excel. It allows you to connect to various data sources (databases, web pages, text files), clean and transform the data, and load it into your spreadsheet. Power Query significantly simplifies data preparation.
Power Pivot: If you’re working with very large datasets or need to combine data from multiple tables, Power Pivot is essential. It’s a data modeling tool that allows you to create relationships between tables, build complex calculations (DAX – Data Analysis Expressions), and analyze massive amounts of information.
Dynamic Arrays: Introduced in recent Excel versions, dynamic arrays automatically spill results across multiple cells based on the formula’s output. This eliminates the need for array formulas enclosed in curly braces {}.
Tips for Troubleshooting
Even power users encounter errors. Here are a few tips to help you troubleshoot:
- Error Checking: Excel’s error checking tool can highlight potential issues in your formulas.
- Formula Auditing: This feature helps trace the dependencies of a formula, allowing you to understand how it arrives at its result and identify any errors.
- Evaluate Formula: Step through a complex formula calculation to see exactly what’s happening at each step.
- Google is your friend: There’s likely someone else who has encountered the same problem and found a solution online.
Conclusion: Mastering Excel takes time and effort, but the rewards are substantial. By embracing these tips and tricks, you can unlock Excel’s full potential and become a true power user, capable of tackling complex data analysis tasks with confidence and efficiency. Don’t be afraid to experiment – the more you explore Excel’s features, the more valuable it will become.



