Nutrition & Diet

Understanding Nutrition & Diet: A Comprehensive Guide
Nutrition and diet – these terms are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct yet interconnected aspects of maintaining health and well-being. This guide aims to delve deep into the world of nutrition and diet, explaining their meanings, importance, key components, and how you can use this knowledge to make informed choices for a healthier life.
What is Nutrition?
At its core, nutrition refers to the process of obtaining and utilizing nutrients from food. These nutrients are essential compounds that our bodies need to function properly – for growth, repair, energy production, and overall health maintenance. It’s not just about *what* you eat, but also how your body processes and utilizes these nutrients.
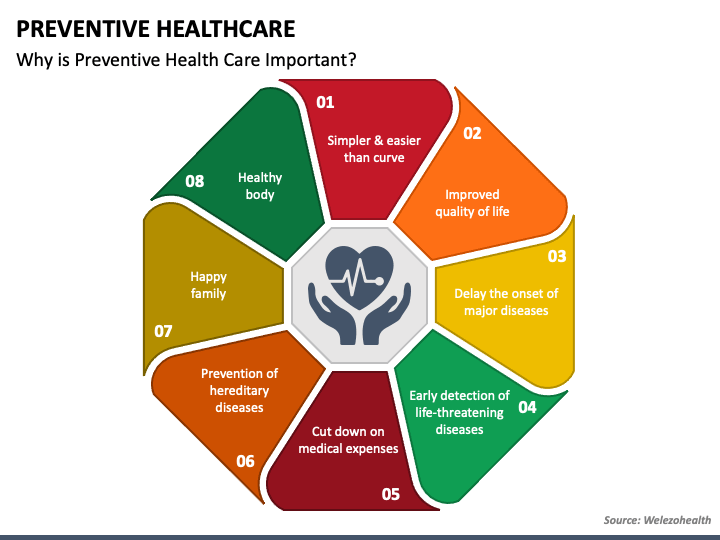
Why is Nutrition Important?
The importance of proper nutrition cannot be overstated. Inadequate or unbalanced nutrition can lead to a wide range of problems, from fatigue and weakened immunity to chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Conversely, good nutrition provides numerous benefits:
- Improved Energy Levels: Adequate nutrient intake fuels your body’s activities throughout the day.
- Stronger Immune System: Vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants bolster your defenses against illness.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: A healthy diet is a cornerstone in preventing many serious health conditions.
- Better Cognitive Function: Nutrients play a vital role in brain health and cognitive performance.
- Healthy Growth and Development: Especially crucial for children and adolescents, proper nutrition supports optimal growth and development.
The Key Components of Nutrition
Let’s break down the essential components that make up good nutrition:
Macronutrients
Macronutrients are nutrients our bodies need in relatively large amounts. They provide energy (measured in calories) and play crucial structural roles.

- Carbohydrates: The body’s primary source of energy. Found in grains, fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. Complex carbohydrates (like whole grains) offer sustained energy release, while simple carbohydrates (like refined sugars) provide a quick burst but lack nutritional value.
- Proteins: Essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting immune function. Good sources include meat, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds. Complete proteins contain all essential amino acids (typically found in animal products), while plant-based proteins may need to be combined to ensure adequate intake of all essential amino acids.
- Fats: Important for hormone production, nutrient absorption, insulation, and protecting organs. Healthy fats include unsaturated fats found in avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon. Saturated and trans fats should be limited.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients are nutrients our bodies need in smaller amounts but are still vital for health.
- Vitamins: Organic compounds that regulate various bodily functions. Examples include Vitamin A (vision), Vitamin C (immune function and antioxidant), and Vitamin D (bone health).
- Minerals: Inorganic substances essential for bone health, nerve function, and many other processes. Examples include calcium, iron, potassium, and zinc.
Water
While not technically a nutrient in the same category as macronutrients or micronutrients, water is absolutely crucial for survival and plays a vital role in virtually every bodily function.
What is Diet?
Diet refers to the pattern of food consumption – what you eat regularly. It’s broader than just nutrition because it encompasses not only *what* you’re eating, but also *when*, *how much*, and even *why*. A healthy diet incorporates principles of good nutrition.
Types of Diets & Dietary Approaches
There are countless dietary approaches, each with its own philosophies and potential benefits. Here are a few examples:
- Mediterranean Diet: Emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fish. It’s associated with numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of heart disease.
- Vegetarian/Vegan Diets: Vegetarian diets exclude meat but may include dairy and eggs. Vegan diets exclude all animal products. Careful planning is needed to ensure adequate intake of nutrients like iron and Vitamin B12 (particularly for vegans).
- Ketogenic Diet: High-fat, very low-carbohydrate diet that forces the body to burn fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. It has shown promise in managing certain conditions like epilepsy but should be approached with caution and under medical supervision.
- Intermittent Fasting: An eating pattern that cycles between periods of eating and voluntary fasting on a regular schedule. There are various methods (e.g., 16/8, 5:2). It may offer benefits for weight management and metabolic health.
Creating a Healthy Diet
Building a healthy diet doesn’t require drastic measures; it’s about making sustainable choices.
- Focus on Whole Foods: Prioritize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Limit Processed Foods: Reduce your intake of processed foods high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium.
- Read Food Labels: Pay attention to serving sizes, nutrient content, and ingredients lists.
- Hydrate Adequately: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Practice Mindful Eating: Pay attention to your hunger cues and eat slowly, savoring each bite.
Individualized Nutrition – Consulting Professionals
It’s important to remember that nutritional needs vary based on factors like age, sex, activity level, health status, and genetics. Consulting with a registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide personalized guidance for creating a diet tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Conclusion
Understanding the principles of nutrition and how they relate to diet is crucial for achieving optimal health and well-being. By making informed food choices, you can nourish your body, prevent disease, and live a longer, healthier life. Remember that small changes over time can lead to significant improvements in your overall health.